The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a European directive aimed at ring-fencing consumer data against illegal or unnecessary access. There is nothing to discuss or debate with local politicians, or the Irish Data Protection Commissioner for that matter. As a European directive, it has over-riding power. To obtain an English version, please visit this link, and select ?EN? from the table of languages.
As you reach for your tea, coffee or Guinness after sighting it, you will be glad to know the Irish Data Protection Commissioner has the lead in turning this into business English we understand. The following diagram should assist you to obtain a quick overview of the process we all have to go through. In this article, we briefly describe what is inside Boxes 1 to 12. The regulation comes into force on 25 May 2018 so we have less than a year to get ready.
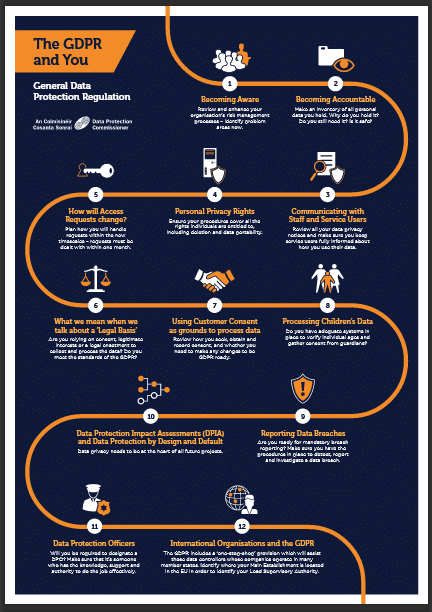
The 12 Essential Steps to Implementing the General Data Protection Act
1. Create awareness among your people of what is coming their way. The GDPR has given our regulator discretion to dish out fines up to ?20,000,000 (or 4% of total annual global turnover, whichever is greater) so there is determination to make this happen.
2. Become accountable by understanding the consumer data you hold. Why are you retaining it, how did you obtain it, and why did you originally collect it. Now you know it is there, how much longer will you still need it? How secure is it in your hands, have you ever shared it?
3. Open a communication channel with your staff, your customers, and anyone else using the data. Share how you feel about how accountable you have been with the information in the past. Explain how you plan to comply with the GDPR in future, and what needs to change.
4. Understand the personal privacy entitlement of the subjects of the information. They have rights to access it, correct mistakes, remove information, restrict its use, decline direct marketing, and copy it to their own files. What needs to change in your systems to assure these rights?
5. Issue a policy for allowing consumers access to their information you hold. You must process requests within a month, and you may not charge for the service unless your cost is excessive. You may decline unfounded or excessive demands within your policy guidelines.
6. Adapt to the requirement that you must have a legal basis for everything you do with, and to consumer data. You need to be in a position to justify your actions to the Irish Data Protection Commissioner in the event of a complaint. Having a legitimate interest is no longer sufficient.
7. Ensure that consumer consent to collect, use, and distribute their data is ?freely given, specific, informed, and unambiguous.? From 25 May 2018 onward, this consent will be your only ground to do so. You cannot force consent. Your benchmark becomes what the GDPR says.
8. Issue rules for managing data of underage subjects. This is currently under review and we are awaiting results. Put systems in place to verify age. Set triggers for where guardians must give consent. Make sure age is verifiable. Use language young people understand.
9. Introduce a culture of openness and honesty, whereby breaches of the GDPR are detected, reported, investigated, and resolved. You will have a duty to file a GDPR report with the Data Protection Commissioner within 72 hours, thus it is important to fast track the process.
10. Introduce a policy of conducting a privacy assessment before taking new initiatives. The GDPR calls for ?privacy by deign?, and we need to engineer it in. This may be the right time to appoint a data controller in your company, and start implementing the GDPR while you have time.
11. You may also need to appoint a data protection officer depending on the size of your business. Alternatively, you need to add managing data protection compliance to an employee?s duties, or appoint an external data-protection compliance consultant.
12. Finally, and you will be glad to know this is the end of the list, the GDPR has an international flavour in that multinational organisations will report into the EU Lead Supervisory Authority. This will manage the process centrally while consulting national data authorities.
The GDPR is a project we all need to complete. If we are out of line, it is in our interests to get things straightened out. Once everything is in place, the task should not be too onerous. Getting there could be the pain.
Contact Us
- (+353)(0)1-443-3807 – IRL
- (+44)(0)20-7193-9751 – UK