When you run a Google search for the “benefits of cloud computing”, you’ll come across a number of articles with a good list of those. However, most of them don’t go into the details, which nevertheless might still suit some readers. But if you’re looking for compelling business reasons to move your company’s IT to the cloud, a peripheral understanding of what this technology can do for you certainly won’t cut it.
Now, cloud computing is not just one of those “cool” technologies that come along every couple of years and which can only benefit a particular department.?What we’re talking about here really is a paradigm shift in computing that can transform not only entire IT infrastructures but also how we run our respective organisations.
I hate to think that some people are holding back on cloud adoption just because they haven’t fully grasped what they’re missing. That is why I decided to put together this list. I wanted to produce a list that would help top management gain a deeper understanding of the benefits of the cloud.
Cloud computing is one bandwagon you really can’t afford not to jump into. Here are ten good reasons why:
1.?Zero?CAPEX and low TCO for an enterprise-class IT infrastructure
2. Improves cash flow
3. Strengthens business continuity/disaster recovery capabilities
4. Lowers the cost of analytics
5. Drives business agility
6. Ushers in anytime, anywhere collaboration
7. Enhances information, product, and service delivery
8. Keeps entire organisation in-sync
9. ?Breathes life into innovation in IT
10. Cultivates optimal environments for development and testing
Zero CAPEX and low TCO for an enterprise-class IT infrastructure
Most cloud adopters with whom I’ve talked to cite this particular reason for gaining interest in the cloud.
Of course they had to dig deeper and consider all other factors before ultimately deciding to migrate. But the first time they heard cloud services could give them access to enterprise class IT infrastructures without requiring any upfront capital investment, they realised this was something worth exploring.
A good IT infrastructure can greatly improve both your cost-effectiveness and your capability to compete with larger companies. The more reliable, fast, highly-available, and powerful it is, the better.
But then building such an infrastructure would normally require a huge capital investment for networking equipment, servers, data storage, power supply, cooling, physical space, and others, which could run up to tens or even hundreds of thousands of euros. To acquire an asset this costly, you’d have to take in debt and be burdened by the ensuing amortisation.
If you’ve got volumes of cash stashed in your vault, cost might not be a problem. But then if you really have so much savings, wouldn’t it be more prudent to use it for other sales-generating projects? An extensive marketing endeavour perhaps?
A capital expenditure of this magnitude and nature, which normally has to be approved by shareholders, can be regarded as a high financial risk. What if business doesn’t do well and you wouldn’t need all that computing power? What if the benefits expected from the IT investment are not realised??You cannot easily convert your IT infrastructure into cash.
Remember we’re talking about a depreciating asset. So even assuming you can liquidate it, you still can’t hope to sell it at its buying price. These factors are going to play in the minds of your Board of Directors when they’re asked to decide on this CAPEX.
Incidentally, these issues don’t exist in a cloud-based solution.
A cloud solution typically follows a pay-as-you-go utility pricing model where you get billed monthly (sometimes quarterly) just like your electricity. ?In other words, it’s an expense you’ll need to pay for?at the end of a period over which the service’s value would have already been realised. Compare that with a traditional infrastructure wherein you’ll have to spend upfront but the corresponding value will still have to be delivered gradually in the succeeding months or years.
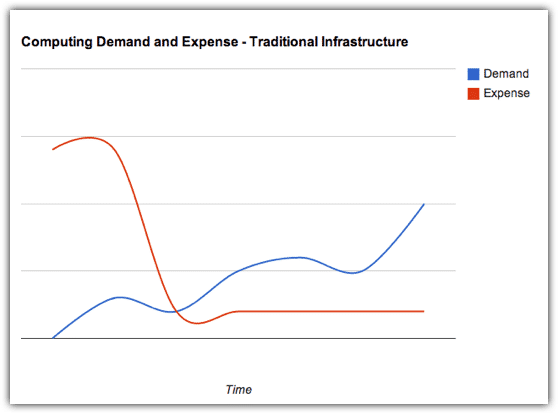
From the point of view of your CFO, what could have been a CAPEX to acquire an asset that depreciates with time (and consequently reduces your company’s net worth), becomes a flexible operating expense (OPEX).?Truly, it is an operating expense that you can increase, decrease, or even totally discontinue, depending on what the prevailing business conditions demand.
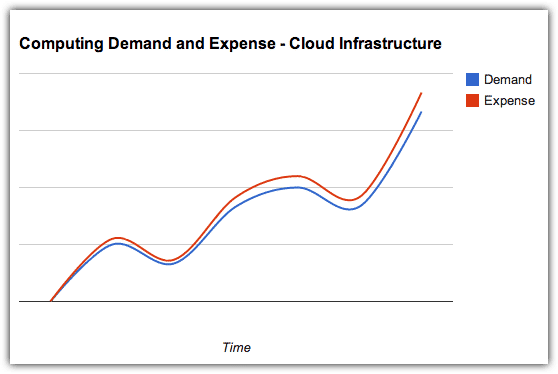
People who think they have done the math in comparing cloud-based and traditional IT infrastructures claim that, although they see how cloud solutions transform CAPEX into OPEX, they really don’t see any significant difference in overall costs.
However, these people have only gone as far as adding up the expected monthly expenses of a cloud solution over the estimated duration of an equivalent IT infrastructure’s effective lifespan and comparing the sum with that IT infrastructure’s price tag. You won’t get a clear comparison that way.
You need to consider all factors that contribute to the infrastructure’s Total Cost of Ownership (TCO). Once you factor in the costs of electricity, floor space, storage, and IT administrators, the economical advantages of choosing a cloud solution will be more evident. Add to that the costs of downtime such as: interruptions to business operations, technical support fees, and the need to maintain expensive IT staff who spend most of their time “firefighting”, and you’ll realise just how big the savings of cloud adopters can be.
Still not convinced? Well, we’re still getting started.?On our next post, we’ll take a closer look at the additional benefits of paying under an OPEX model instead of a CAPEX model.
Contact Us
-
(+353)(0)1-443-3807 – IRL
-
(+44)(0)20-7193-9751 – UK

