DevOps ? a clipped compound of development and operations – is a way of working whereby software developers are in a team with project beneficiaries. A client centred approach extends the project plan to include the life cycle of the product or service, for which the software is developed.
We can then no longer speak of a software project for say Joe?s Accounting App. The software has no intrinsic value of its own. It follows that the software engineers are building an accounting app product. This is a small, crucially important distinction, because they are no longer in a silo with different business interests.
To take the analogy further, the developers are no longer contractors possibly trying to stretch out the process. They are members of Joe?s accounting company, and they are just as keen to get to market fast as Joe is to start earning income. DevOps uses this synergy to achieve the overarching business goal.
A Brief Introduction to OpsDev
You can skip this section if you already read this article. If not then you need to know that DevOps is a culture, not a working method. The three ?members? are the software developers, the beneficiaries, and a quality control mechanism. The developers break their task into smaller chunks instead of releasing the code to quality control as a single batch. As a result, the review process happens contiguously along these simplified lines.
| Code | QC | Test | ? | ? | ? |
| ? | Code | QC | Test | ? | ? |
| ? | ? | Code | QC | Test | ? |
| ? | ? | ? | Code | QC | Test |
| Colour Key | Developers | Quality Control | Beneficiary |
This is a marked improvement over the previously cumbersome method below.
| Write the Code | ? | Test the Code | ? | Use the Code |
| ? | Evaluate, Schedule for Next Review | ? | ||
Working quickly and releasing smaller amounts of code means the OpsDev team learns quickly from mistakes, and should come to product release ahead of any competitor using the older, more linear method. The shared method of working releases huge resources in terms of user experience and in-line QC practices. Instead of being in a silo working on its own, development finds it has a richer brief and more support from being ?on the same side of the organisation?.
The Key Role that Application Program Interfaces Play
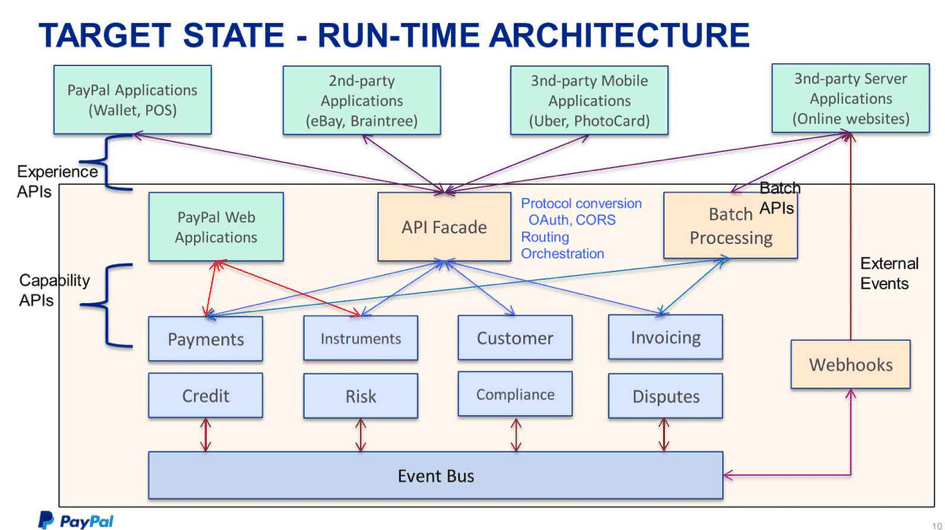
Application Program Interfaces, or API?s for short, are building blocks for software applications. Using proprietary software-bridges speeds this process up. A good example would be the PayPal applications that we find on so many websites today. API?s are not just for commercial sites, and they can reduce costs and improve efficiency considerably.
The following diagram courtesy of TIBCO illustrates how second-party applications integrate with PayPal architecture via an API fa?ade.
Working quickly and releasing smaller amounts of code means the OpsDev team learns quickly from mistakes, and should come to product release ahead of any competitor using the older, more linear method. The shared method of working releases huge resources in terms of user experience and in-line QC practices. Instead of being in a silo working on its own, development finds it has a richer brief and more support from being ?on the same side of the organisation?.
The DevOps Revolution Continues ?
We close with some important insights from an interview with Jim Stoneham. He was general manager of the Yahoo Communities business unit, at the time Flickr became a part. ?Flickr was a codebase,? Jim recalls, ?that evolved to operate at high scale over 7 years – and continuing to scale while adding and refining features was no small challenge. During this transition, it was a huge advantage that there was such an integrated dev and ops team?
The ?maturity model? as engineers refer to DevOps status currently, enables developers to learn faster, and deploy upgrades ahead of their competitors. This means the client reaches and exceeds break-even sooner. DevOps lubricates the value chain so companies add value to a product faster. One reason it worked so well with Flickr, was the immense trust between Dev and Ops, and that is a lesson we should learn.
?We transformed from a team of employees to a team of owners. When you move at that speed, and are looking at the numbers and the results daily, your investment level radically changes. This just can’t happen in teams that release quarterly, and it’s difficult even with monthly cycles.? (Jim Stoneham)
Contact Us
- (+353)(0)1-443-3807 – IRL
- (+44)(0)20-7193-9751 – UK