You buy the latest iPhone on credit. Turn to fast car loan services to get yourself those wheels you’ve been eyeing for a while. Take out a mortgage to realise your dream of being a homeowner. Regardless of the motive, the common denominator is going into financial debt to achieve something today, and pay it off in future, with interest. The final cost will be higher than the loan value that you took out in the first place. However, debt is not limited to the financial world.
Technical Debt Definition
Technical debt – which is also referred to as code debt, design debt or tech debt – is the result of the development team taking shortcuts in the code to release a product today, which will need to be fixed later on. The quality of the code takes a backseat to issues like market forces, such as when there’s pressure to get a product out there to beat a deadline, front-run the competition, or even calm jittery consumers. Creating perfect code would take time, so the team opts for a compromised version, which they will come back later to resolve. It’s basically using a speedy temporary fix instead of waiting for a more comprehensive solution whose development would be slower.
How rampant is it? 25% of the development time in large software organisations is actually spent dealing with tech debt, according to a multiple case study of 15 organizations. “Large” here means organizations with over 250 employees. It is estimated that global technical debt will cost companies $4 trillion by 2024.
Is there interest on technical debt?
When you take out a mortgage or service a car loan, the longer that it takes to clear it the higher the interest will be. A similar case applies to technical debt. In the rush to release the software, it comes with problems like bugs in the code, incompatibility with some applications that would need it, absent documentation, and other issues that pop up over time. This will affect the usability of the product, slow down operations – and even grind systems to a halt, costing your business. Here’s the catch: just like the financial loan, the longer that one takes before resolving the issues with rushed software, the greater the problems will pile up, and more it will take to rectify and implement changes. This additional rework that will be required in future is the interest on the technical debt.
Reasons For Getting Into Technical Debt
In the financial world, there are good and bad reasons for getting into debt. Taking a loan to boost your business cashflow or buy that piece of land where you will build your home – these are understandable. Buying an expensive umbrella on credit because ‘it will go with your outfit‘ won’t win you an award for prudent financial management. This also applies to technical debt.
There are situations where product delivery takes precedence over having completely clean code, such as for start-ups that need their operations to keep running for the brand to remain relevant, a fintech app that consumers rely on daily, or situations where user feedback is needed for modifications to be made to the software early. On the other hand, incurring technical debt because the design team chooses to focus on other products that are more interesting, thus neglecting the software and only releasing a “just-usable” version will be a bad reason.
Some of the common reasons for technical debt include:
- Inadequate project definition at the start – Where failing to accurately define product requirements up-front leads to software development that will need to be reworked later
- Business pressure – Here the business is under pressure to release a product, such as an app or upgrade quickly before the required changes to the code are completed.
- Lacking a test suite – Without the environment to exhaustively check for bugs and apply fixes before the public release of a product, more resources will be required later to resolve them as they arise.
- Poor collaboration – From inadequate communication amongst the different product development teams and across the business hierarchy, to junior developers not being mentored properly, these will contribute to technical debt with the products that are released.
- Lack of documentation – Have you launched code without its supporting documentation? This is a debt that will need to be fulfilled.
- Parallel development – This is seen when working on different sections of a product in isolation which will, later on, need to be merged into a single source. The greater the extent of modification on an individual branch – especially when it affects its compatibility with the rest of the code, the higher the technical debt.
- Skipping industrial standards – If you fail to adhere to industry-standard features and technologies when developing the product, there will be technical debt because you will eventually need to rework the product to align with them for it to continue being relevant.
- Last-minute product changes – Incorporating changes that hadn’t been planned for just before its release will affect the future development of the product due to the checks, documentation and modifications that will be required later on
Types of Technical Debt
There are various types of technical debt, and this will largely depend on how you look at it.
- Intentional technical debt – which is the debt that is consciously taken on as a strategy in the business operations.
- Unintentional technical debt – where the debt is non-strategic, usually the consequences of a poor job being done.
This is further expounded in the Technical Debt Quadrant” put forth by Martin Fowler, which attempts to categorise it based on the context and intent:
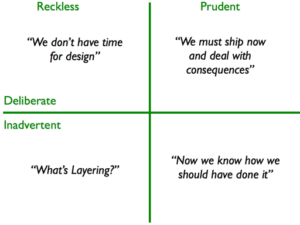
Source: MartinFowler.com
Final thoughts
Technical debt is common, and not inherently bad. Just like financial debt, it will depend on the purpose that it has been taken up, and plans to clear it. Start-ups battling with pressure to launch their products and get ahead, software companies that have cut-throat competition to deliver fast – development teams usually find themselves having to take on technical debt instead of waiting to launch the products later. In fact, nearly all of the software products in use today have some sort of technical debt.
But no one likes being in debt. Actually, technical staff often find themselves clashing with business executives as they try to emphasise the implications involved when pushing for product launch before the code is completely ready. From a business perspective, it’s all about weighing the trade-offs, when factoring in aspects such as the aspects market situation, competition and consumer needs. So, is technical debt good or bad? It will depend on the context. Look at it this way: just like financial debt, it is not a problem as long as it is manageable. When you exceed your limits and allow the debt to spiral out of control, it can grind your operations to a halt, with the ripple effects cascading through your business.